Cho hàm số \(f(x) = \dfrac{x+2}{x^{2}-9}\) có đồ thị như trên hình 53.
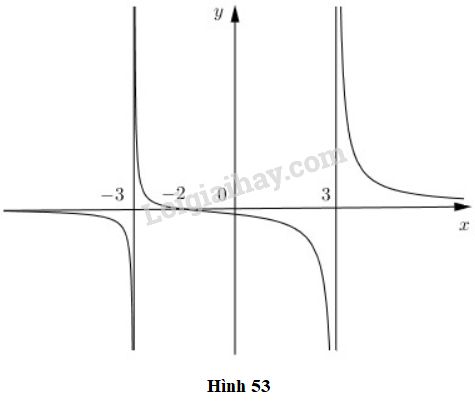
a) Quan sát đồ thị và nêu nhận xét về giá trị hàm số đã cho khi \(x → -∞\), \(x → 3^-\) và \(x → -3^+\)
b) Kiểm tra các nhận xét trên bằng cách tính các giới hạn sau:
\(\underset{x\rightarrow -\infty }{\lim} f(x)\) với \(f(x)\) được xét trên khoảng \((-\infty; -3)\),
\(\underset{x\rightarrow 3^{-}}{\lim} f(x)\) với \(f(x)\) được xét trên khoảng \((-3,3)\),
\(\underset{x\rightarrow -3^{+}}{\lim} f(x)\) với \(f(x)\) được xét trên khoảng \((-3; 3)\).