Bài 3.31 trang 178 SBT giải tích 12
Tính diện tích hình phẳng giới hạn bởi các đường sau:
a) \(\displaystyle y = 2x - {x^2},x + y = 2\);
b) \(\displaystyle y = {x^3} - 12x,y = {x^2}\);
c) \(\displaystyle x + y = 1;x + y = - 1;\) \(\displaystyle x - y = 1;x - y = - 1\);
d) \(\displaystyle y = \frac{1}{{1 + {x^2}}},y = \frac{1}{2}\)
e) \(\displaystyle y = {x^3} - 1\) và tiếp tuyến với \(\displaystyle y = {x^3} - 1\) tại điểm \(\displaystyle \left( { - 1; - 2} \right)\).
Lời giải
a) \(\displaystyle y = 2x - {x^2},x + y = 2\)
Ta có: \(\displaystyle y = 2x - {x^2},y = 2 - x\)
Phương trình hoành độ giao điểm: \(\displaystyle 2x - {x^2} = 2 - x\) \(\displaystyle \Leftrightarrow {x^2} - 3x + 2 = 0 \Leftrightarrow \left[ \begin{array}{l}x = 1\\x = 2\end{array} \right.\)
Khi đó diện tích \(\displaystyle S = \int\limits_1^2 {\left| {2x - {x^2} - 2 + x} \right|dx} \) \(\displaystyle = \int\limits_1^2 {\left| { - {x^2} + 3x - 2} \right|dx} \) \(\displaystyle = \int\limits_1^2 {\left( { - {x^2} + 3x - 2} \right)dx} \)
\(\displaystyle = \left. {\left( { - \frac{{{x^3}}}{3} + \frac{3}{2}{x^2} - 2x} \right)} \right|_1^2\) \(\displaystyle = - \frac{8}{3} + 6 - 4 + \frac{1}{3} - \frac{3}{2} + 2 = \frac{1}{6}\)
Vậy \(\displaystyle S = \frac{1}{6}\).
b) \(\displaystyle y = {x^3} - 12x,y = {x^2}\)
Phương trình hoành độ giao điểm:
\(\displaystyle {x^3} - 12x = {x^2}\)\(\displaystyle \Leftrightarrow {x^3} - {x^2} - 12x = 0\) \(\displaystyle \Leftrightarrow x\left( {{x^2} - x - 12} \right) = 0\) \(\displaystyle \Leftrightarrow \left[ \begin{array}{l}x = 0\\{x^2} - x - 12 = 0\end{array} \right.\) \(\displaystyle \Leftrightarrow \left[ \begin{array}{l}x = 0\\x = - 3\\x = 4\end{array} \right.\)
Diện tích là:
\(\displaystyle S = \int\limits_{ - 3}^4 {\left| {{x^3} - 12x - {x^2}} \right|dx} \) \(\displaystyle = \int\limits_{ - 3}^0 {\left| {{x^3} - 12x - {x^2}} \right|dx} \) \(\displaystyle + \int\limits_0^4 {\left| {{x^3} - 12x - {x^2}} \right|dx} \)
\(\displaystyle = \left| {\int\limits_{ - 3}^0 {\left( {{x^3} - {x^2} - 12x} \right)dx} } \right|\) \(\displaystyle + \left| {\int\limits_0^4 {\left( {{x^3} - {x^2} - 12x} \right)dx} } \right|\) \(\displaystyle = \frac{{99}}{4} + \frac{{160}}{3} = \frac{{937}}{{12}}\).
Vậy \(\displaystyle S = \frac{{937}}{{12}}\).
c) \(\displaystyle x + y = 1;x + y = - 1;\) \(\displaystyle x - y = 1;x - y = - 1\);
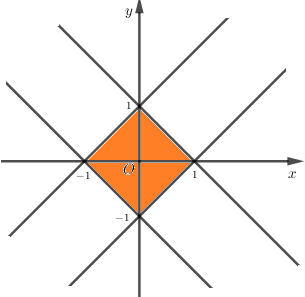
Vẽ các đường thẳng \(\displaystyle x + y = 1;x + y = - 1;\) \(\displaystyle x - y = 1;x - y = - 1\) trên hệ tục tọa độ ta được phần cần tính diện tích là hình vuông có các đỉnh \(\displaystyle \left( { - 1;0} \right),\left( {0; - 1} \right),\left( {1;0} \right),\left( {0;1} \right)\).
Diện tích hình vuông là: \(\displaystyle S = 4.\frac{1}{2}.1.1 = 2\).
Chú ý:
Sử dụng công thức tích phân ta được \(\displaystyle S = 4\int\limits_0^1 {\left( {1 - x} \right)dx} \)\(\displaystyle = 4\left. {\left( {x - \frac{{{x^2}}}{2}} \right)} \right|_0^1 = 4\left( {1 - \frac{1}{2}} \right) = 2\).
d) \(\displaystyle y = \frac{1}{{1 + {x^2}}},y = \frac{1}{2}\)
Ta có: \(\displaystyle \frac{1}{{1 + {x^2}}} = \frac{1}{2}\)\(\displaystyle \Leftrightarrow 1 + {x^2} = 2\) \(\displaystyle \Leftrightarrow {x^2} = 1 \Leftrightarrow x = \pm 1\).
Diện tích: \(\displaystyle S = \int\limits_{ - 1}^1 {\left| {\frac{1}{{1 + {x^2}}} - \frac{1}{2}} \right|dx} \)\(\displaystyle = \int\limits_{ - 1}^1 {\left( {\frac{1}{{1 + {x^2}}} - \frac{1}{2}} \right)dx} \)
Dễ thấy hàm số \(\displaystyle y = \frac{1}{{{x^2} + 1}} - \frac{1}{2}\) là hàm số chẵn nên \(\displaystyle S = \int\limits_{ - 1}^1 {\left( {\frac{1}{{1 + {x^2}}} - \frac{1}{2}} \right)dx} \) \(\displaystyle = 2\int\limits_0^1 {\left( {\frac{1}{{1 + {x^2}}} - \frac{1}{2}} \right)dx} \)
Xét \(\displaystyle I = \int\limits_0^1 {\left( {\frac{1}{{1 + {x^2}}} - \frac{1}{2}} \right)dx} \)\(\displaystyle = \int\limits_0^1 {\frac{{dx}}{{1 + {x^2}}}} - \frac{1}{2}\int\limits_0^1 {dx} \) \(\displaystyle = J - \frac{1}{2}\) với \(\displaystyle J = \int\limits_0^1 {\frac{1}{{1 + {x^2}}}dx} \)
Đặt \(\displaystyle x = \tan t \Rightarrow dx = \left( {1 + {{\tan }^2}t} \right)dt\) \(\displaystyle \Rightarrow J = \int\limits_0^{\frac{\pi }{4}} {\frac{{1 + {{\tan }^2}t}}{{1 + {{\tan }^2}t}}dt} = \frac{\pi }{4}\)\(\displaystyle \Rightarrow I = \frac{\pi }{4} - \frac{1}{2}\)
Vậy \(\displaystyle S = 2I = 2.\left( {\frac{\pi }{4} - \frac{1}{2}} \right) = \frac{\pi }{2} - 1\).
e) \(\displaystyle y = {x^3} - 1\) và tiếp tuyến với \(\displaystyle y = {x^3} - 1\) tại điểm \(\displaystyle \left( { - 1; - 2} \right)\).
Xét \(\displaystyle y = g\left( x \right) = {x^3} - 1\) có \(\displaystyle g'\left( x \right) = 3{x^2}\)\(\displaystyle \Rightarrow g'\left( { - 1} \right) = 3\).
Phương trình tiếp tuyến của đồ thị hàm số \(\displaystyle y = g\left( x \right)\) tại điểm \(\displaystyle \left( { - 1; - 2} \right)\) là:
\(\displaystyle y = 3\left( {x + 1} \right) - 2\) hay \(\displaystyle y = 3x + 1\).
Xét phương trình \(\displaystyle {x^3} - 1 = 3x + 1 \Leftrightarrow {x^3} - 3x - 2 = 0\) \(\displaystyle \Leftrightarrow \left( {x - 2} \right){\left( {x + 1} \right)^2} = 0 \Leftrightarrow \left[ \begin{array}{l}x = - 1\\x = 2\end{array} \right.\)
Diện tích: \(\displaystyle S = \int\limits_{ - 1}^2 {\left| {{x^3} - 3x - 2} \right|dx} \) \(\displaystyle = \int\limits_{ - 1}^2 {\left( { - {x^3} + 3x + 2} \right)dx} \) \(\displaystyle = \left. {\left( { - \frac{{{x^4}}}{4} + \frac{3}{2}{x^2} + 2x} \right)} \right|_{ - 1}^2\) \(\displaystyle = - 4 + 6 + 4 + \frac{1}{4} - \frac{3}{2} + 2 = \frac{{27}}{4}\).
Vậy \(\displaystyle S = \frac{{27}}{4}\).
- Bài 3.31 trang 178 SBT giải tích 12
- Bài 3.32 trang 178 SBT giải tích 12
- Bài 3.33 trang 178 SBT giải tích 12
- Bài 3.34 trang 178 SBT giải tích 12
- Bài 3.35 trang 178 SBT giải tích 12
- Bài 3.36 trang 179 SBT giải tích 12
- Bài 3.37 trang 179 SBT giải tích 12
- Bài 3.38 trang 179 SBT giải tích 12
- Bài 3.39 trang 180 SBT giải tích 12
- Bài 3.40 trang 180 SBT giải tích 12
- Bài 3.41 trang 180 SBT giải tích 12
- Bài 3.42 trang 180 SBT giải tích 12
