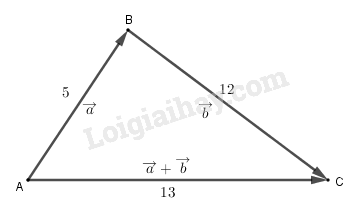
Dựng tam giác ABC có AB = 5, BC= 12 và AC = 13.
Ta có \(\left| {\overrightarrow a } \right| = 5,\left| {\overrightarrow b } \right| = 12\) và \(\left| {\overrightarrow a + \overrightarrow b } \right| = 13\)
Và \(\overrightarrow {AB} = \overrightarrow a ,\overrightarrow {BC} = \overrightarrow b ,\overrightarrow {AC} = \overrightarrow a + \overrightarrow b \). Khi đó \(\overrightarrow a (\overrightarrow a + \overrightarrow b ) = \overrightarrow {AB} .\overrightarrow {AC} \).
Mặt khác ta có:
\(\overrightarrow {AB} .\overrightarrow {AC} = \dfrac{1}{2}\left( {A{C^2} + A{B^2} - B{C^2}} \right)\)\( = \dfrac{1}{2}\left( {{{13}^2} + {5^2} - {{12}^2}} \right) = 25\)
Ta suy ra \(\cos \left( {\overrightarrow {AB} ,\overrightarrow {AC} } \right) = \dfrac{{\overrightarrow {AB} .\overrightarrow {AC} }}{{\left| {\overrightarrow {AB} } \right|.\left| {\overrightarrow {AC} } \right|}}\)\( = \dfrac{{25}}{{5.13}} \approx 0,3846\)
Suy ra \(\left( {\overrightarrow {AB} ,\overrightarrow {AC} } \right) \approx {67^0}{23^'}\).
Chú ý :
Có thể nhận xét tam giác \(ABC\) vuông tại \(B\) nên \(\overrightarrow {AB} .\overrightarrow {BC} = 0\).
Từ đó \(\overrightarrow {AB} .\left( {\overrightarrow {AB} + \overrightarrow {BC} } \right)\) \( = \overrightarrow {AB} .\overrightarrow {AB} + \overrightarrow {AB} .\overrightarrow {BC} \) \( = A{B^2} + 0 = 25\).